The Power of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG): A Game Changer in the Energy Industry
Introduction
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) has revolutionized the energy industry, offering a cleaner and more efficient fuel source. In this blog post, we will explore the various aspects of LNG, including its production process, advantages, environmental impact, global market trends, and future prospects.
See More The Cons Of Lng Collection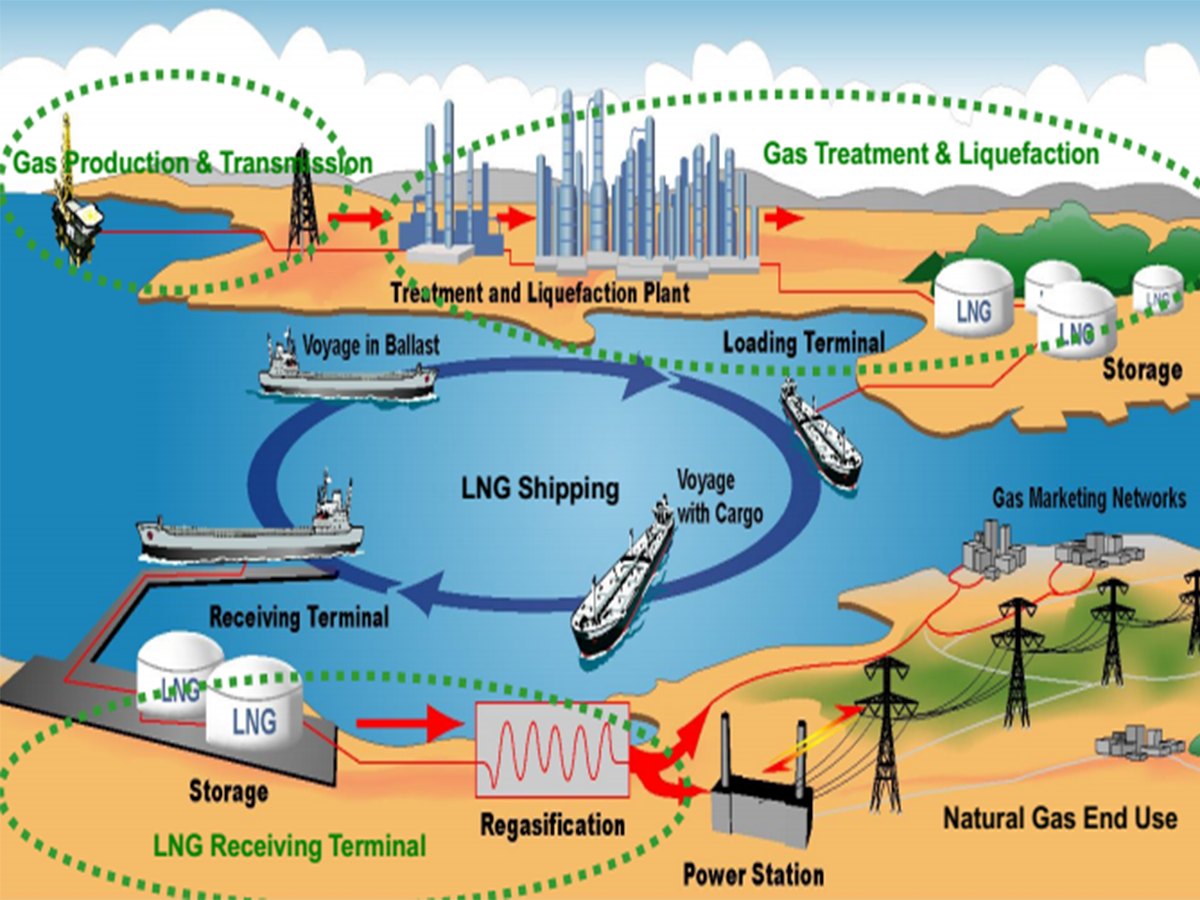
Section 1: Understanding Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
LNG is the liquid form of natural gas obtained by cooling it to a temperature of around -162 degrees Celsius. The liquefaction process reduces the volume of natural gas by about 600 times, making it easier to store and transport. This transformation into LNG allows for long-distance transportation and enables access to remote locations that are not connected to pipelines.
More About Us: SOUTHERN GAS TRADING JSC
Section 2: Production Process of LNG
The production of LNG involves several stages, starting with the extraction of natural gas from underground reservoirs. Once extracted, impurities like water, sulfur compounds, and carbon dioxide are removed through a purification process. The natural gas is then cooled to its liquefaction point using a specialized cryogenic process. After liquefaction, the LNG is stored in insulated tanks until it is ready for transportation.
Section 3: Advantages of Using LNG
3.1 Environmental Benefits
Compared to other fossil fuels, LNG has lower carbon dioxide emissions, virtually no sulfur dioxide emissions, and significantly reduced nitrogen oxide emissions. This makes it a much cleaner alternative for power generation and transportation, contributing to improved air quality and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
3.2 Energy Efficiency
LNG is highly energy-efficient due to its high energy density. When compared to traditional fuels like diesel or gasoline, LNG provides more energy per unit of volume. This increased efficiency translates into cost savings and reduced fuel consumption.
3.3 Versatility and Flexibility
LNG can be used in various sectors, including power generation, heating, transportation, and industrial processes. It can serve as a replacement for more polluting fuels such as coal or oil in power plants and can be used as a fuel for ships, trucks, and trains. Its versatility and flexibility make it a valuable resource across multiple industries.
Section 4: Environmental Impact of LNG
While LNG offers environmental benefits compared to other fossil fuels, it is important to consider the entire lifecycle of LNG production, including extraction, liquefaction, transportation, and regasification. The extraction process may have environmental implications such as habitat disruption and methane leaks. Additionally, the transportation of LNG via tankers consumes energy and emits greenhouse gases. However, advancements in technology are continuously improving the industry's environmental performance.
Section 5: Global Market Trends in LNG
5.1 Increasing Demand
The demand for LNG has been steadily rising due to its affordability, environmental benefits, and versatility. Developing countries are increasingly adopting LNG as a cleaner alternative to traditional fuels, while developed nations are integrating it into their energy mix to reduce emissions.
5.2 Expanding Infrastructure
To meet the growing demand for LNG, there has been significant investment in infrastructure development. This includes the construction of liquefaction plants, regasification terminals, and storage facilities. These infrastructure developments enable countries to import and export LNG efficiently.
5.3 Emerging Exporters and Importers
Traditionally dominated by a few major players, the LNG market has seen the emergence of new exporters such as the United States and Australia. On the import side, countries like China and India have become major consumers of LNG as they seek to diversify their energy sources and reduce pollution levels.
Section 6: Future Prospects of LNG
The future of LNG looks promising as the world transitions towards a more sustainable energy landscape. Here are some key factors shaping its future prospects:
6.1 Renewable Integration
LNG can play a vital role in facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources like wind and solar into existing power grids. It can act as a backup fuel during periods of low renewable energy production or when grid stability is required.
6.2 Green Technologies
Advancements in green technologies are making LNG production even more environmentally friendly. From carbon capture and storage to more efficient liquefaction processes, these innovations will further reduce the carbon footprint associated with LNG.
6.3 New Markets and Applications
The demand for LNG is expected to grow beyond traditional sectors such as power generation and transportation. Applications such as floating LNG terminals for offshore gas fields and small-scale LNG for remote areas or marine bunkering are gaining traction.
Conclusion
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) has emerged as a game-changer in the energy industry due to its environmental benefits, energy efficiency, versatility, and growing global market demand. As the world seeks cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions, LNG is poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of our energy landscape.
#what_is_the_lng, #pgscomvn, #pgs_com_vn, #whatisthelng, #what_is_the_lng, #pgscomvn, #pgs_com_vn/

Nhận xét
Đăng nhận xét