The Power of LNG: Unleashing the Potential of Liquefied Natural Gas
Description: In this blog post, we will explore the world of liquefied natural gas (LNG) and its immense potential as a clean and versatile energy source. From its production to its transportation and utilization, we will dive deep into the various aspects of LNG and highlight its importance in shaping the future of energy.
See More What Is The Lng Collection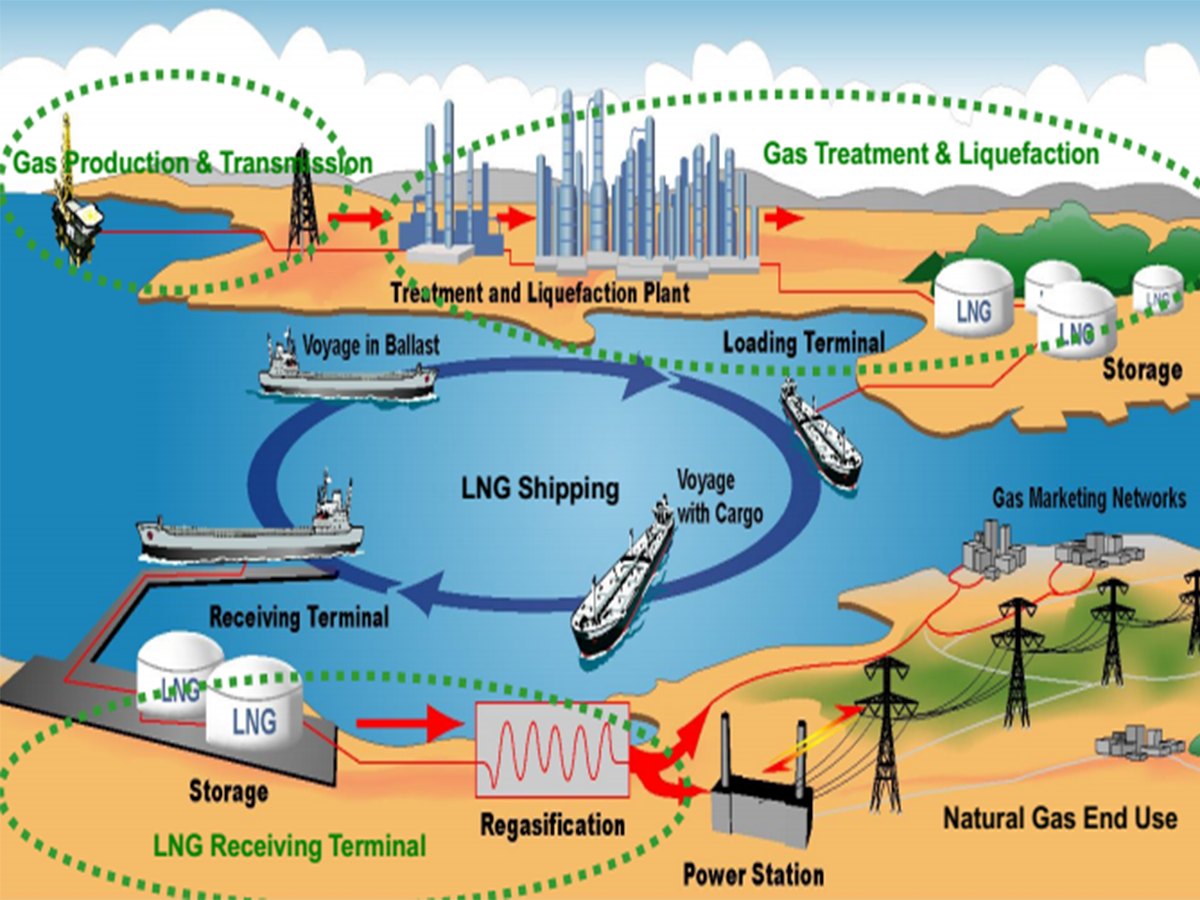
Section 1: Introduction to LNG
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is a clear, colorless, and non-toxic liquid form of natural gas that is produced by cooling natural gas to extremely low temperatures (-162°C or -260°F) at atmospheric pressure. This process reduces the volume of the gas by around 600 times, making it easier and more economical to transport and store.
More About Us: SOUTHERN GAS TRADING JSC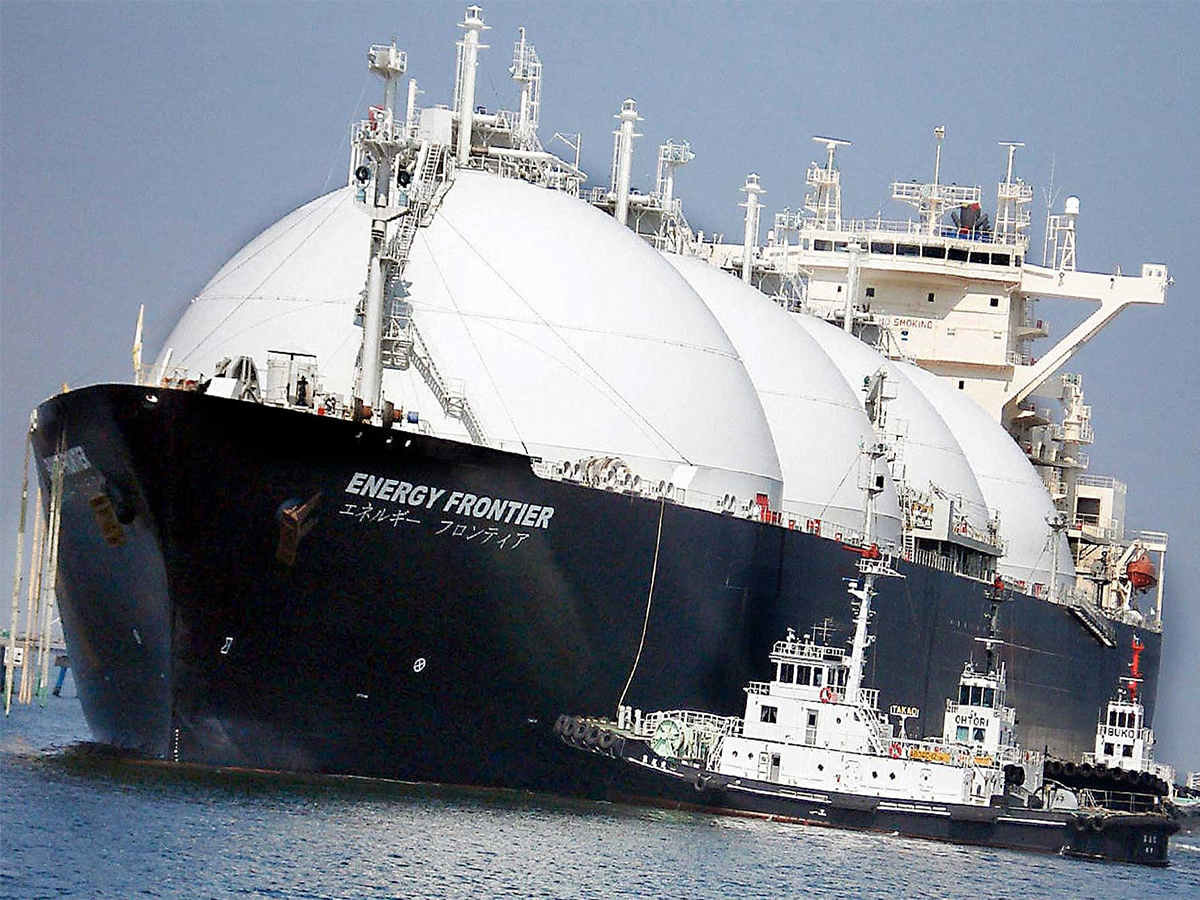
LNG is primarily composed of methane, with small amounts of other hydrocarbons such as ethane, propane, and butane. It is odorless and non-corrosive, making it a safer alternative to other fossil fuels.
Section 2: The LNG Value Chain
The LNG value chain consists of several interconnected stages, each playing a vital role in bringing LNG from its source to end-users:
2.1 Exploration and Production
The journey of LNG begins with the exploration and production of natural gas. Natural gas fields are identified and drilling operations are carried out to extract the raw gas.
2.2 Processing and Liquefaction
Once the natural gas is extracted, impurities such as water, carbon dioxide, and sulfur compounds are removed through a process called gas processing. The processed natural gas then undergoes liquefaction through a cooling process that converts it into LNG.
2.3 LNG Transportation
LNG transportation involves loading the liquefied gas onto specialized carriers called LNG tankers or vessels. These vessels are designed to maintain the low temperatures required to keep the gas in its liquid state during transit.
2.4 Storage and Regasification
Upon reaching its destination, LNG is transferred to storage tanks where it is kept at cryogenic temperatures until it is ready for regasification. Regasification is the process of converting LNG back into its gaseous form for distribution.
2.5 Distribution and Utilization
Regasified natural gas can be transported through pipelines or via trucks for distribution to various end-users such as power plants, industrial facilities, residential areas, or used as fuel for transportation.
Section 3: Advantages of LNG
LNG offers numerous advantages over traditional energy sources. Let's explore some of the key benefits:
3.1 Environmental Benefits
LNG is considered a cleaner burning fuel compared to coal and oil. When combusted, it produces significantly lower levels of harmful emissions such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and greenhouse gases (GHGs). This makes it an attractive option for reducing air pollution and combating climate change.
3.2 Energy Efficiency
The liquefaction process removes impurities and reduces the volume of natural gas, making it more energy-dense. This increased energy density allows for more efficient storage and transportation, enabling greater energy security and flexibility in supply.
3.3 Versatility in Applications
LNG can be used across a wide range of sectors, including power generation, heating, cooking, transportation, and industrial processes. Its versatility makes it a valuable energy source for both developed and developing countries with varying energy needs.
3.4 Economic Benefits
LNG provides economic benefits by diversifying energy sources, reducing reliance on imported oil, and creating new opportunities for job growth and investment in infrastructure development. It also helps stabilize energy prices by tapping into global gas markets.
Section 4: Global LNG Market
The global LNG market has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven by increasing demand for cleaner energy sources. Let's take a closer look at the key players and trends shaping the market:
4.1 Major LNG Exporters
Countries such as Qatar, Australia, the United States, Russia, and Malaysia are among the largest exporters of LNG. These nations possess vast natural gas reserves and have invested heavily in liquefaction infrastructure.
4.2 Emerging Markets
Emerging markets like China, India, Bangladesh, and Pakistan are witnessing a surge in LNG demand due to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and growing energy needs. These countries are increasingly turning to LNG as a cleaner alternative to coal and oil.
4.3 Technological Advancements
Advancements in liquefaction technologies have made LNG production more efficient and cost-effective. Floating LNG (FLNG) facilities have also emerged as a viable solution for offshore gas fields that were previously uneconomical to develop.
4.4 Infrastructure Development
To meet the growing demand for LNG, significant investments are being made in developing infrastructure such as liquefaction plants, regasification terminals, storage tanks, and transportation networks. These developments are crucial for expanding the global LNG trade.
Section 5: Challenges and Future Outlook
While LNG presents numerous benefits, there are also challenges that need to be addressed:
5.1 Environmental Concerns
Although LNG is cleaner than many other fossil fuels, there are still concerns regarding methane leakage during production, transportation, and handling. Efforts are being made to minimize these emissions through improved technology and best practices.
5.2 Infrastructure Requirements
Expanding the LNG market requires substantial investments in infrastructure development. Establishing liquefaction plants, regasification terminals, pipelines, and storage facilities involves significant capital expenditure and long lead times.
5.3 Price Volatility
The price of LNG is influenced by factors such as supply-demand dynamics, geopolitical tensions, and oil prices since they are often linked through long-term contracts. Price volatility can impact project economics and hinder market growth.
Despite these challenges, the future outlook for LNG remains promising:
The International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts that global LNG demand will continue to rise significantly in the coming years due to increasing energy needs, environmental concerns, and expanding access to gas markets. Investments in infrastructure and technology advancements are expected to further drive the growth of the global LNG market.
In conclusion, LNG is a game-changer in the world of energy. Its environmental benefits, energy efficiency, versatility, and economic advantages make it a crucial component in transitioning towards a more sustainable future. With ongoing advancements in technology and infrastructure development, the potential for LNG as a clean and accessible energy source is set to soar in the years ahead.
#what_is_the_lng, #pgscomvn, #pgs_com_vn, #whatisthelng, #what_is_the_lng, #pgscomvn, #pgs_com_vn/

Nhận xét
Đăng nhận xét